基本数据结构
单链表
// head存储链表头,e[]存储节点的值,ne[]存储节点的next指针,idx表示当前用到了哪个节点
int head, e[N], ne[N], idx;
// 初始化
void init()
{
head = -1;
idx = 0;
}
// 在链表头插入一个数a
void insert(int a)
{
e[idx] = a, ne[idx] = head, head = idx ++ ;
}
// 将头结点删除,需要保证头结点存在
void remove()
{
head = ne[head];
}双链表
// e[]表示节点的值,l[]表示节点的左指针,r[]表示节点的右指针,idx表示当前用到了哪个节点
int e[N], l[N], r[N], idx;
// 初始化
void init()
{
//0是左端点,1是右端点
r[0] = 1, l[1] = 0;
idx = 2;
}
// 在节点a的右边插入一个数x
void insert(int a, int x)
{
e[idx] = x;
l[idx] = a, r[idx] = r[a];
l[r[a]] = idx, r[a] = idx ++ ;
}
// 删除节点a
void remove(int a)
{
l[r[a]] = l[a];
r[l[a]] = r[a];
}
栈
// tt表示栈顶
int stk[N], tt = 0;
// 向栈顶插入一个数
stk[ ++ tt] = x;
// 从栈顶弹出一个数
tt -- ;
// 栈顶的值
stk[tt];
// 判断栈是否为空
if (tt > 0)
{
}队列
普通队列
// hh 表示队头,tt表示队尾
int q[N], hh = 0, tt = -1;
// 向队尾插入一个数
q[ ++ tt] = x;
// 从队头弹出一个数
hh ++ ;
// 队头的值
q[hh];
// 判断队列是否为空
if (hh <= tt)
{
}循环队列
// hh 表示队头,tt表示队尾的后一个位置
int q[N], hh = 0, tt = 0;
// 向队尾插入一个数
q[tt ++ ] = x;
if (tt == N) tt = 0;
// 从队头弹出一个数
hh ++ ;
if (hh == N) hh = 0;
// 队头的值
q[hh];
// 判断队列是否为空
if (hh != tt)
{
}KMP 算法
// s[]是长文本,p[]是模式串,n是s的长度,m是p的长度
求模式串的Next数组:
for (int i = 2, j = 0; i <= m; i ++ )
{
while (j && p[i] != p[j + 1]) j = ne[j];
if (p[i] == p[j + 1]) j ++ ;
ne[i] = j;
}
// 匹配
for (int i = 1, j = 0; i <= n; i ++ )
{
while (j && s[i] != p[j + 1]) j = ne[j];
if (s[i] == p[j + 1]) j ++ ;
if (j == m)
{
j = ne[j];
// 匹配成功后的逻辑
}
}
Trie 树
int son[N][26], cnt[N], idx;
// 0号点既是根节点,又是空节点
// son[][]存储树中每个节点的子节点
// cnt[]存储以每个节点结尾的单词数量
// 插入一个字符串
void insert(char *str)
{
int p = 0;
for (int i = 0; str[i]; i ++ )
{
int u = str[i] - 'a';
if (!son[p][u]) son[p][u] = ++ idx;
p = son[p][u];
}
cnt[p] ++ ;
}
// 查询字符串出现的次数
int query(char *str)
{
int p = 0;
for (int i = 0; str[i]; i ++ )
{
int u = str[i] - 'a';
if (!son[p][u]) return 0;
p = son[p][u];
}
return cnt[p];
}
// 结构体写法
struct node{
node* son[26];
int cnt = 0;
};
node* head = new node();
void insert(string s) {
node* p = head;
for (int i = 0; i < s.size(); ++ i) {
int u = s[i] - 'a';
if (p->son[u] == NULL) {
p->son[u] = new node();
}
p = p->son[u];
}
p->cnt ++;
}
bool query(string& s, int idx, int f) {
node* p = head;
for (int i = 0; i < s.size(); ++ i) {
int u = s[i] - 'a';
if (p->son[u] == NULL) return false;
p = p->son[u];
}
return p->cnt > 0;
}
并查集
(1)朴素并查集:
int p[N]; //存储每个点的祖宗节点
// 返回x的祖宗节点
int find(int x)
{
if (p[x] != x) p[x] = find(p[x]);
return p[x];
}
// 初始化,假定节点编号是1~n
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) p[i] = i;
// 合并a和b所在的两个集合:
p[find(a)] = find(b);
(2)维护size的并查集:
int p[N], size[N];
//p[]存储每个点的祖宗节点, size[]只有祖宗节点的有意义,表示祖宗节点所在集合中的点的数量
// 返回x的祖宗节点
int find(int x)
{
if (p[x] != x) p[x] = find(p[x]);
return p[x];
}
// 初始化,假定节点编号是1~n
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ )
{
p[i] = i;
size[i] = 1;
}
// 合并a和b所在的两个集合:
size[find(b)] += size[find(a)];
p[find(a)] = find(b);
(3)维护到祖宗节点距离的并查集:
int p[N], d[N];
//p[]存储每个点的祖宗节点, d[x]存储x到p[x]的距离
// 返回x的祖宗节点
int find(int x)
{
if (p[x] != x)
{
int u = find(p[x]);
d[x] += d[p[x]];
p[x] = u;
}
return p[x];
}
// 初始化,假定节点编号是1~n
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ )
{
p[i] = i;
d[i] = 0;
}
// 合并a和b所在的两个集合:
p[find(a)] = find(b);
d[find(a)] = distance; // 根据具体问题,初始化find(a)的偏移量
板子
struct DSU{
vector<int> p;
DSU(int n) : p(n + 1){
iota(p.begin(), p.end(), 0);
}
int find(int x){
return p[x] == x ? x : p[x] = find(p[x]);
}
bool same(int x, int y) {
return find(x) == find(y);
}
bool merge(int x, int y){
x = find(x), y = find(y);
if (x == y) return false;
p[y] = x;
return true;
}
};
堆
// h[N]存储堆中的值, h[1]是堆顶,x的左儿子是2x, 右儿子是2x + 1
// ph[k]存储第k个插入的点在堆中的位置
// hp[k]存储堆中下标是k的点是第几个插入的
int h[N], ph[N], hp[N], size;
// 交换两个点,及其映射关系
void heap_swap(int a, int b)
{
swap(ph[hp[a]],ph[hp[b]]);
swap(hp[a], hp[b]);
swap(h[a], h[b]);
}
void down(int u)
{
int t = u;
if (u * 2 <= size && h[u * 2] < h[t]) t = u * 2;
if (u * 2 + 1 <= size && h[u * 2 + 1] < h[t]) t = u * 2 + 1;
if (u != t)
{
heap_swap(u, t);
down(t);
}
}
void up(int u)
{
while (u / 2 && h[u] < h[u / 2])
{
heap_swap(u, u / 2);
u >>= 1;
}
}
// O(n)建堆
for (int i = n / 2; i; i -- ) down(i);
一般哈希
(1) 拉链法
int h[N], e[N], ne[N], idx;
// 向哈希表中插入一个数
void insert(int x)
{
int k = (x % N + N) % N;
e[idx] = x;
ne[idx] = h[k];
h[k] = idx ++ ;
}
// 在哈希表中查询某个数是否存在
bool find(int x)
{
int k = (x % N + N) % N;
for (int i = h[k]; i != -1; i = ne[i])
if (e[i] == x)
return true;
return false;
}
(2) 开放寻址法
int h[N];
// 如果x在哈希表中,返回x的下标;如果x不在哈希表中,返回x应该插入的位置
int find(int x)
{
int t = (x % N + N) % N;
while (h[t] != null && h[t] != x)
{
t ++ ;
if (t == N) t = 0;
}
return t;
}
字符串哈希
核心思想:将字符串看成P进制数,P的经验值是131或13331,取这两个值的冲突概率低
小技巧:取模的数用2^64,这样直接用unsigned long long存储,溢出的结果就是取模的结果
typedef unsigned long long ULL;
ULL h[N], p[N]; // h[k]存储字符串前k个字母的哈希值, p[k]存储 P^k mod 2^64
// 初始化
p[0] = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ )
{
h[i] = h[i - 1] * P + str[i];
p[i] = p[i - 1] * P;
}
// 计算子串 str[l ~ r] 的哈希值
ULL get(int l, int r)
{
return h[r] - h[l - 1] * p[r - l + 1];
}高级数据结构
ST 表
详细理论
ST[p][i] 表示从 i 点开始共${2^p}$ 个数的最大值,即[i, i + ${2^p}$ - 1] 区间最大值
void ST(){
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i ++) st[0][i] = x[i];
int p = log(n) / log(2);
for(int k = 1; k <= p; k ++){
for(int i = 1; i + (1 << k) - 1 <= n; i ++){
st[k][i] = max(st[k - 1][i], st[k - 1][i + (1 << (k - 1))]);
}
}
}
int query(int l, int r){
int p = __lg(r - l + 1);
// int p = log(r - l + 1) / log(2);
return max(st[p][l], st[p][r - (1 << p) + 1]);
}树状数组
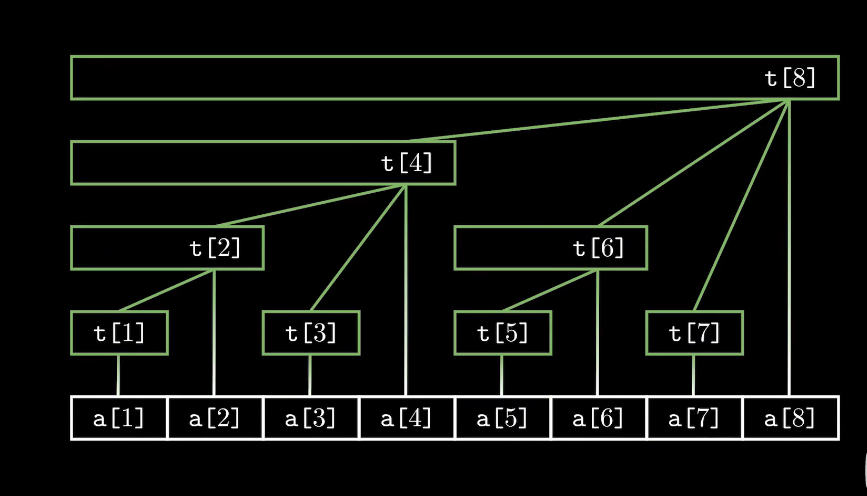
typedef long long LL;
int a[N]; // a 是需要维护的数组
LL tr[N];
int lowbit(int x)
{
return x & -x;
}
void add(LL c[], int x, int v)
{
for (int i = x; i <= n; i += lowbit(i))
c[i] += v;
}
LL query(LL c[], int x)
{
LL res = 0;
for (int i = x; i; i -= lowbit(i))
res += c[i];
return res;
}
int main() {
// 原地 O(n)建树状数组
for (int x = 1; x <= n; ++x)
for (int i = x - 1; i > x - lowbit(x); i -= lowbit(i))
tr[x] += tr[i];
}线段树
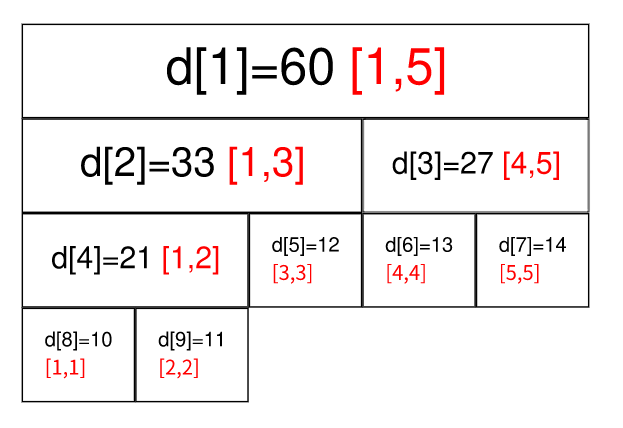
typedef long long LL;
int w[N]; // 要维护的数组
struct Node
{
int l, r;
LL sum, add; // 依据情况自定义变量
}tr[N * 4];
void pushup(int u) {
// 自定义
}
void pushdowm(int u) {
// 自定义
}
// 左闭右闭
void build(int u, int l, int r) {
if (l == r) tr[u] = {l, r, w[l], 0};
else {
tr[u] = {l, r};
int mid = l + r >> 1;
build(u << 1, 1, mid), build(u << 1 | 1, mid + 1, r);
pushup(u);
}
}
void modify(int u, int l, int r) {
if (l <= tr[u].l && tr[u].r <= r)
{
// 自定义
}
else
{
pushdown(u);
int mid = tr[u].l + tr[u].r >> 1;
if (l <= mid) modify(u << 1, l, r);
if (r > mid) modify(u << 1 | 1, l, r);
pushup(u);
}
}
LL query(int u, int l, int r)
{
if (l <= tr[u].l && tr[u].r <= r) {
// 自定义
}
pushdown(u);
int mid = tr[u].l + tr[u].r >> 1;
LL v = 0;
if (l <= mid) v = query(u << 1, l, r);
if (r > mid) v += query(u << 1 | 1, l, r);
return v;
}
int main() {
// 左闭右闭,编号从 1 开始
bulid(1, 1, n);
}动态开点线段树
#define ls(u) tr[u].L
#define rs(u) tr[u].R
class RangeModule {
static const int N = 1E6;
struct node{
int l, r;
int L, R;
int sum = 0;
int f = 0;
}tr[4 * N];
int idx = 1;
void push_up(int u) {
tr[u].sum = tr[ls(u)].sum + tr[rs(u)].sum;
}
void push_dowm(int u) {
int& L = ls(u), &R = rs(u);
if (!L) {
L = ++ idx;
tr[L] = {tr[u].l, tr[u].l + tr[u].r >> 1};
}
if (!R) {
R = ++ idx;
tr[R] = {(tr[u].l + tr[u].r >> 1) + 1, tr[u].r};
}
if (tr[u].f == 0) return;
else if (tr[u].f == -1) {
tr[L].sum = 0;
tr[R].sum = 0;
}else {
int len = tr[u].r - tr[u].l + 1;
tr[L].sum = len - len / 2;
tr[R].sum = len / 2;
}
tr[L].f = tr[u].f;
tr[R].f = tr[u].f;
tr[u].f = 0;
}
void update(int u, int l, int r, int f) {
if (l <= tr[u].l && tr[u].r <= r) {
tr[u].f = f;
if (f == 1)
tr[u].sum = tr[u].r - tr[u].l + 1;
else tr[u].sum = 0;
return;
}
int mid = tr[u].r + tr[u].l >> 1;
push_dowm(u);
if (l <= mid) update(ls(u), l, r, f);
if (r > mid) update(rs(u), l, r, f);
push_up(u);
}
int query(int u, int l, int r) {
if (l <= tr[u].l && tr[u].r <= r) {
return tr[u].sum;
}
int mid = tr[u].l + tr[u].r >> 1;
push_dowm(u);
int ret = 0;
if (l <= mid) ret += query(ls(u), l, r);
if (r > mid) ret += query(rs(u), l, r);
return ret;
}
public:
RangeModule() {
tr[1] = {1, 1000000005};
}
void addRange(int left, int right) {
update(1, left, right - 1, 1);
}
bool queryRange(int left, int right) {
// if (left == 13 && right == 15) cout << query(1, 13, 14) << endl;
return query(1, left, right - 1) == (right - left);
}
void removeRange(int left, int right) {
update(1, left, right - 1, -1);
}
};
/**
* Your RangeModule object will be instantiated and called as such:
* RangeModule* obj = new RangeModule();
* obj->addRange(left,right);
* bool param_2 = obj->queryRange(left,right);
* obj->removeRange(left,right);
*/珂朵莉树
struct Node {
int l, r;
mutable int v;
Node(const int &il, const int &ir, const int &iv) : l(il), r(ir), v(iv) {}
inline bool operator<(const Node &o) const { return l < o.l; }
};
set<Node> odt;
const int n = 1e9;
auto split(int x) {
if (x > n) return odt.end();
auto it = odt.lower_bound(Node{x, 0, 0});
if (it != odt.end() && it->l == x) return it;
--it;
int l = it->l, r = it->r, v = it->v;
odt.erase(it);
odt.insert(Node(l, x - 1, v));
return odt.insert(Node(x, r, v)).first;
}
void assign(int l, int r, int v) {
auto itr = split(r + 1), itl = split(l);
odt.erase(itl, itr);
odt.insert(Node(l, r, v));
}
int query(int l, int r) {
auto itr = split(r + 1), itl = split(l);
int res = 0;
for (; itl != itr; ++itl) {
res += (itl->r - itl->l + 1) * itl->v;
}
return res;
}平衡树
Treap
简概:每个节点包含 key 值 和 随机生成的 val 值,满足 按 key 的二叉搜索树 的同时 满足 按 val 的小(或大)顶堆 的性质
struct node{
int l, r;
int key, val;
int cnt, sz; // 自定义
}tr[N];
int idx, root;
void push_up(int p) {
tr[p].sz = tr[tr[p].l].sz + tr[tr[p].r].sz + tr[p].cnt;
// 自定义
}
int get_node(int x) {
tr[++ idx].key = x;
tr[idx].val = rand();
tr[idx].cnt = tr[idx].sz = 1;
return idx;
}
// 左旋
void zag(int& p) {
int q = tr[p].r;
tr[p].r = tr[q].l, tr[q].l = p, p = q;
push_up(tr[p].l), push_up(p);
}
// 右旋
void zip(int& p) {
int q = tr[p].l;
tr[p].l = tr[q].r, tr[q].r = p, p = q;
push_up(tr[p].r), push_up(p);
}
void built() {
get_node(INF), get_node(-INF); // 两个哨子节点
root = 1;
tr[root].l = 2;
push_up(root);
if (tr[1].val < tr[2].val) zip(root); // 这里是 val 的小顶堆
}
void insert(int& p, int x) {
if (!p) p = get_node(x);
else if (tr[p].key == x) tr[p].cnt ++;
else if (tr[p].key < x) {
insert(tr[p].r, x);
if (tr[tr[p].r].val > tr[p].val) zag(p);
}else {
insert(tr[p].l, x);
if (tr[tr[p].l].val > tr[p].val) zip(p);
}
push_up(p);
}
void del(int& p, int key) {
if (!p) return;
if (tr[p].key == key) {
if (tr[p].cnt > 1) {
tr[p].cnt --;
}
else if (tr[p].l || tr[p].r ) {
if (!tr[p].r || tr[tr[p].l].val > tr[tr[p].r].val) {
zip(p);
del(tr[p].r, key);
}else {
zag(p);
del(tr[p].l, key);
}
}else p = 0;
}else if (key > tr[p].key) {
del(tr[p].r, key);
}
else {
del(tr[p].l, key);
}
push_up(p);
}
int look_for_rank(int p, int x) {
if (tr[p].key == x) {
return tr[tr[p].l].sz + 1;
}
else if (x < tr[p].key) {
return look_for_rank(tr[p].l, x);
}
else {
return tr[tr[p].l].sz + tr[p].cnt + look_for_rank(tr[p].r, x);
}
}
Splay
简概:每操作一次后,将该操作后的节点旋转到根节点
struct node{
int s[2], p, v; // s: 两个子节点编号, p: 父节点编号 v:当前点权值
int sz, flag;
void init(int _v, int _p) {
v = _v, p = _p;
sz = 1;
}
}tr[N];
int root, idx;
void pushup(int u) {
tr[u].sz = tr[tr[u].s[0]].sz + tr[tr[u].s[1]].sz + 1;
// 自定义
}
void pushdown(int u) {
if (tr[u].flag) {
swap(tr[u].s[0], tr[u].s[1]);
tr[tr[u].s[0]].flag ^= 1;
tr[tr[u].s[1]].flag ^= 1;
tr[u].flag = 0;
}
}
// 左右旋合并写法
void rotate(int u) {
int y = tr[u].p, z = tr[y].p;
int k = tr[y].s[1] == u;
tr[z].s[tr[z].s[1] == y] = u, tr[u].p = z;
tr[y].s[k] = tr[u].s[k ^ 1], tr[tr[u].s[k ^ 1]].p = y;
tr[u].s[k ^ 1] = y, tr[y].p = u;
pushup(u), pushup(y);
}
void splay(int u, int k) {
while (tr[u].p != k) {
int y = tr[u].p, z = tr[y].p;
if (z != k) {
if ((tr[y].s[1] == u) ^ (tr[z].s[1] == y) ) rotate(u);
else rotate(y);
}
rotate(u);
}
if (!k) root = u;
}
// 插入一个数
void insert(int v) {
int u = root, p = 0;
while (u) {
p = u, u = tr[u].s[v > tr[u].v];
}
u = ++ idx; // 节点编号从 1 开始
if (p) tr[p].s[v > tr[p].v] = u;
tr[u].init(v, p);
splay(u, 0); // 转到 根节点
}
莫队
简概:1.分块;2.每个处理区间按左端点的所在块排序,右端点从左到右排序;3.处理每个操作区间
树链剖分
简概:1.根据子节点的权值大小分为重轻儿子;2.当前节点连向重儿子为重边,其余轻边; 3.重边 构成的极大路径为重链
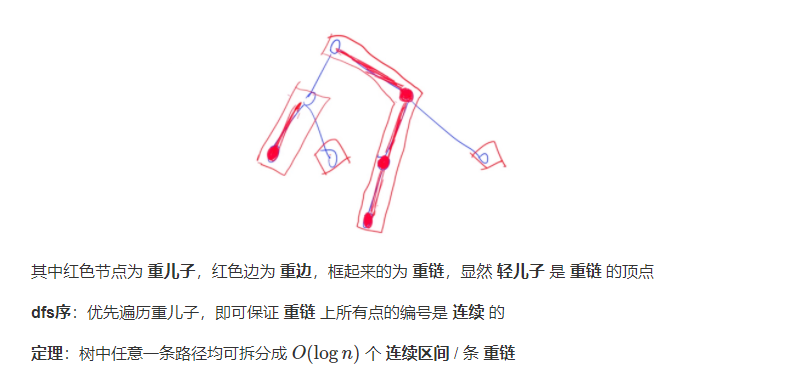
int h[N], w[N], e[M], ne[M], idx; //建树
int id[N], nw[N], cnt; //id:节点的dfn序编号,nw[id[i]]是i的权值w(w -> nw的映射)
int dep[N], sz[N], top[N], fa[N], son[N];
//sz:子树节点个数,top:重链的顶点,son:重儿子,fa:父节点
struct SegmentTree
{
int l, r;
LL sum, flag;
}tr[N << 2];
void add(int a, int b)
{
e[idx] = b, ne[idx] = h[a], h[a] = idx ++ ;
}
//dfs1预处理
void dfs1(int u, int father, int depth)
{
dep[u] = depth, fa[u] = father, sz[u] = 1;
for (int i = h[u]; ~i; i = ne[i])
{
int j = e[i];
if (j == father) continue;
dfs1(j, u, depth + 1);
sz[u] += sz[j];
if (sz[son[u]] < sz[j]) son[u] = j; //重儿子是子树节点最多的儿子
}
}
//dfs2做剖分(t是重链的顶点)
void dfs2(int u, int t)
{ // id 为每个节点分配编号, nw 为 w 的映射, top 为当前节点 u 的重链顶点
id[u] = ++ cnt, nw[cnt] = w[u], top[u] = t;
if (!son[u]) return; //叶节点结束
dfs2(son[u], t); //重儿子重链剖分
//处理轻儿子
for (int i = h[u]; ~i; i = ne[i])
{
int j = e[i];
if (j == fa[u] || j == son[u]) continue;
dfs2(j, j); //轻儿子的重链顶点就是他自己
}
}
//------------------------线段树的部分------------------------\\
void pushup(int u)
{
tr[u].sum = tr[u << 1].sum + tr[u << 1 | 1].sum;
}
void pushdown(int u)
{
auto &root = tr[u], &left = tr[u << 1], &right = tr[u << 1 | 1];
if (root.flag)
{
left.sum += root.flag * (left.r - left.l + 1);
left.flag += root.flag;
right.sum += root.flag * (right.r - right.l + 1);
right.flag += root.flag;
root.flag = 0;
}
}
void build(int u, int l, int r)
{
tr[u] = {l, r, nw[r], 0};
if (l == r) return;
int mid = l + r >> 1;
build(u << 1, l, mid), build(u << 1 | 1, mid + 1, r);
pushup(u);
}
void update(int u, int l, int r, int k)
{
if (l <= tr[u].l && r >= tr[u].r)
{
tr[u].flag += k;
tr[u].sum += k * (tr[u].r - tr[u].l + 1);
return;
}
pushdown(u);
int mid = tr[u].l + tr[u].r >> 1;
if (l <= mid) update(u << 1, l, r, k);
if (r > mid) update(u << 1 | 1, l, r, k);
pushup(u);
}
LL query(int u, int l, int r)
{
if (l <= tr[u].l && r >= tr[u].r) return tr[u].sum;
pushdown(u);
int mid = tr[u].l + tr[u].r >> 1;
LL res = 0;
if (l <= mid) res += query(u << 1, l, r);
if (r > mid) res += query(u << 1 | 1, l, r);
return res;
}
//------------------------线段树的部分------------------------\\
void update_path(int u, int v, int k)
{
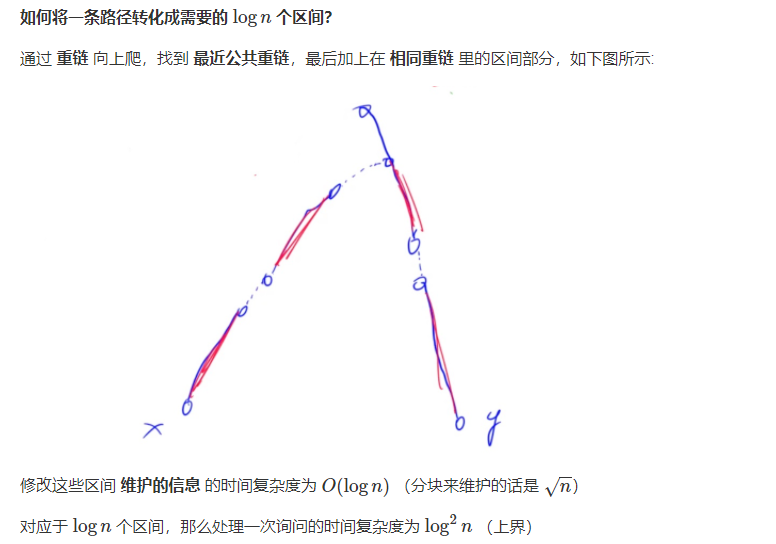
while (top[u] != top[v]) //向上爬找到相同重链
{
if (dep[top[u]] < dep[top[v]]) swap(u, v);
update(1, id[top[u]], id[u], k); //dfs序原因,上面节点的id必然小于下面节点的id
u = fa[top[u]];
}
if (dep[u] < dep[v]) swap(u, v);
update(1, id[v], id[u], k); //在同一重链中,处理剩余区间
}
LL query_path(int u, int v)
{
LL res = 0;
while (top[u] != top[v]) //向上爬找到相同重链
{
if (dep[top[u]] < dep[top[v]]) swap(u, v);
res += query(1, id[top[u]], id[u]);
u = fa[top[u]];
}
if (dep[u] < dep[v]) swap(u, v);
res += query(1, id[v], id[u]); //在同一重链中,处理剩余区间
return res;
}
void update_tree(int u, int k) //子树全部加上k
{
update(1, id[u], id[u] + sz[u] - 1, k); //由于dfs序的原因,可以利用子树节点个数直接找到区间
}
LL query_tree(int u)
{
return query(1, id[u], id[u] + sz[u] - 1); //原因同上
}
int main() {
// 预处理
dfs1(1, -1, 1);
// 树链剖分
dfs2(1, 1);
// 线段树维护
build(1, 1, n);
}
动态树
简概:1.任意选一条连向子节点的边为实边;2.实边构成的极大路径为实链;3.用 Splay 维护每个实链
参考文章

struct Splay
{
int s[2], p, v;
int sum, rev; // 自定义
}tr[N];
bool isroot(int u) //判断 u 是否为实链的顶部
{
return tr[tr[u].p].s[0] != u && tr[tr[u].p].s[1] != u;
}
//------------------Splay系函数------------------\\
void pushup(int u)
{
tr[u].sum = tr[tr[u].s[0]].sum ^ tr[u].v ^ tr[tr[u].s[1]].sum;
}
void pushrev(int u)
{
swap(tr[u].s[0], tr[u].s[1]);
tr[u].rev ^= 1;
}
void pushdown(int u)
{
if (tr[u].rev)
{
pushrev(tr[u].s[0]);
pushrev(tr[u].s[1]);
tr[u].rev = 0;
}
}
void rotate(int x)
{
int y = tr[x].p, z = tr[y].p;
int k = tr[y].s[1] == x;
if (!isroot(y)) tr[z].s[tr[z].s[1] == y] = x; //唯一的不同处
tr[x].p = z;
tr[y].s[k] = tr[x].s[k ^ 1], tr[tr[x].s[k ^ 1]].p = y;
tr[x].s[k ^ 1] = y, tr[y].p = x;
pushup(y), pushup(x);
}
void splay(int x) //迭代写法
{
static int stk[N]; //先自上而下下传懒标记
int tt = 0, t = x;
stk[ ++ tt] = t;
while (!isroot(t)) stk[ ++ tt] = t = tr[t].p;
while (tt) pushdown(stk[tt -- ]);
//接下来基本与splay板子相同
while (!isroot(x))
{
int y = tr[x].p, z = tr[y].p;
if (!isroot(y))
if ((tr[z].s[1] == y) ^ (tr[y].s[1] == x)) rotate(x);
else rotate(y);
rotate(x);
}
}
//------------------Splay系函数------------------\\
void access(int x) //建立一条从根节点到 x 的实链(同时将 x 变成对应 splay 的根节点)
{
int z = x; //记录初始的节点编号
for (int y = 0; x; y = x, x = tr[x].p) //x沿着虚边往上找根
{
splay(x); //先转到当前辅助树的根
tr[x].s[1] = y, pushup(x); //把上个树接到中序遍历后面
}
splay(z); //把初始的节点转到根
}
void makeroot(int x) //将 x 变成原树的根节点(且左子树为空)
{
access(x); //此时x为辅助树的根节点,直接反转中序遍历即可
pushrev(x);
}
int findroot(int x) //找到 x 所在的原树的根节点,再将原树的根节点旋转到辅助树的根节点
{
access(x); //打通根节点到 x 的实链,当前 x 位于辅助树的根节点位置
while (tr[x].s[0]) pushdown(x), x = tr[x].s[0]; //找到辅助树中序遍历的第一个元素(左下角)
splay(x); //转到根节点
return x;
}
void split(int x, int y) //将 x 到 y 的路径变为实边路径
{
makeroot(x); //先把 x 设为根
access(y); //在打通根到 y 的实链即可
}
void link(int x, int y) //若 x , y 不连通,则加入 (x, y) 这条边
{
makeroot(x); //先把 x 设为根
if (findroot(y) != x) tr[x].p = y; //如果不连通,则把 x 的实链接到 y 上即可
}
void cut(int x, int y) //若边 (x, y) 存在,则删掉(x, y)这条边
{
makeroot(x);
if (findroot(y) == x && tr[x].s[1] == y && !tr[y].s[0])
{
tr[y].p = tr[x].s[1] = 0;
pushup(x);
}
}
左偏树
简概:每个节点有一个 dist, 表示当前节点到空节点的最近距离。其中左节点的 dist 大于右节点的 dist;
struct T{
int l, r, v, d, f;
// l, r 表示左右儿子, v 表示值
// d 表示从当前节点到最近叶子节点的距离, f 表示当前节点的父亲
} t[N];
int find(int x) {
return t[x].f == x ? x : t[x].f = find(t[x].f);
}
int merge(int x, int y) { // 递归合并函数
if (!x || !y) return x + y;
if (t[x].v > t[y].v || (t[x].v == t[y].v && x > y)) swap(x, y);
rs = merge(rs, y);
if (t[ls].d < t[rs].d) swap(ls, rs);
t[x].d = t[rs].d + 1;
return x;
}
int work(int x, int y) { // 合并 x, y 两个堆。
if (x == y) return 0;
if (!x || !y) return t[x + y].f = x + y;
if (t[x].v > t[y].v || (t[x].v == t[y].v && x > y)) swap(x, y);
t[x].f = t[y].f = x;
merge(x, y); return x;
}
void del(int x) { // 删除一个数
t[x].f = work(ls, rs);
}后缀数组
//x--存储第一关键字
//y--存储第二关键字
//c--存储每个数值的数目
//rk--rk[i]表示从i开始的后缀的排名
//sa--sa[i]表示排名为i的后缀的起始下标
//h--h[i]表示排名为i的后缀和排名为i - 1的后缀的最长前缀
int x[N], y[N], c[N], rk[N], sa[N], h[N];
char s[N];
void get_sa(){
for(int i = 1 ; i <= n ; ++i) c[x[i] = s[i]]++;
for(int i = 2 ; i <= m ; ++i) c[i] += c[i - 1];
for(int i = n ; i ; --i) sa[c[x[i]]--] = i;
for(int k = 1 ; k <= n ; k <<= 1){
int num = 0;
//先按照第二关键字排序,下标从i开始的后缀的第二关键字为从i+k开始的第一关键字
//先将无第二关键字的后缀排先名,此时y[i]表示按照第二关键字排名为i的起始下标
for(int i = n - k + 1 ; i <= n ; ++i) y[++num] = i;
for(int i = 1 ; i <= n ; ++i){
//上一层循环中按照第一关键字的排名的下标已经存在sa数组中
//按从小到大顺序枚举sa数组可保证按照第一关键字从小到大
//所有起始下标超过k才存在第二关键字
//将所有存在第二关键字的后缀存储在y数组中,此时是按i + k的第一关键字,下标要-k
if(sa[i] > k) y[++num] = sa[i] - k;
}
//将计数数组清空
for(int i = 1 ; i <= m ; ++i) c[i] = 0;
for(int i = 1 ; i <= n ; ++i) c[x[i]]++;
for(int i = 2 ; i <= m ; ++i) c[i] += c[i - 1];
//y数组存储的是按照第二关键字从小到大排序后的后缀的起始下标
//i从大到小枚举即可保证按照第一关键字排序后依然是按照第二关键字排序后的相对顺序不变
for(int i = n ; i ; --i) sa[c[x[y[i]]]--] = y[i],y[i] = 0;
swap(x,y),num = 1;
//将所有后缀离散化
x[sa[1]] = 1;
//此时y存储的是从i开始的后缀的第一关键字
for(int i = 2 ; i <= n ; ++i){
//若当前后缀和排名前一位的后缀第一关键字和第二关键字相同则离散化后的数值相同,否则+1
x[sa[i]] = (y[sa[i]] == y[sa[i - 1]] and y[sa[i] + k] == y[sa[i - 1] + k]) ? num : ++num;
}
if(num == n) break;
m = num;
}
}
void get_h(){
for(int i = 1 ; i <= n ; ++i) rk[sa[i]] = i;
for(int i = 1,k = 0 ; i <= n ; ++i){
if(rk[i] == 1) continue;
//h[rk[i]] >= h[rk[i - 1]] - 1
if(k) k--;
//j为排名前一位的起始下标
int j = sa[rk[i] - 1];
//求最长相同前缀
while(i + k <= n and j + k <= n and s[i + k] == s[j + k]) k++;
h[rk[i]] = k;
}
}